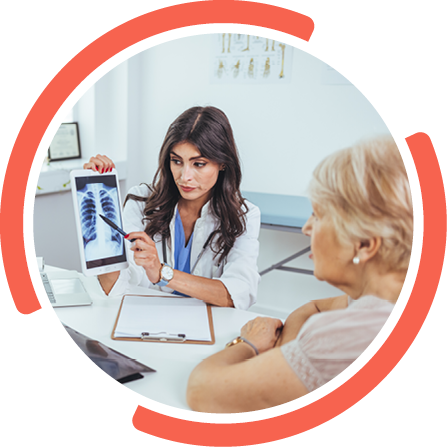

The primary purpose of specimens intended for initial diagnoses is to make an accurate diagnosis and preserve tissue for molecular studies
In resection specimens, the primary purpose is to classify the histologic subtype and determine staging1*
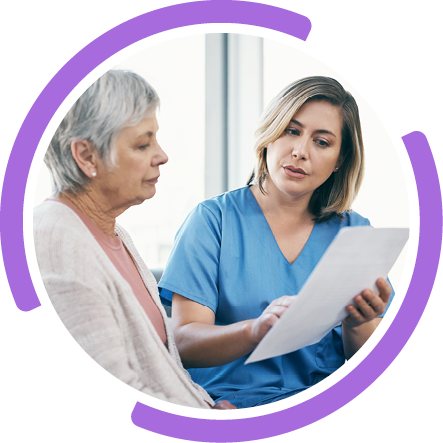

Broad molecular profiling should be carried out on samples to help identify patients that may be eligible for targeted therapies1*
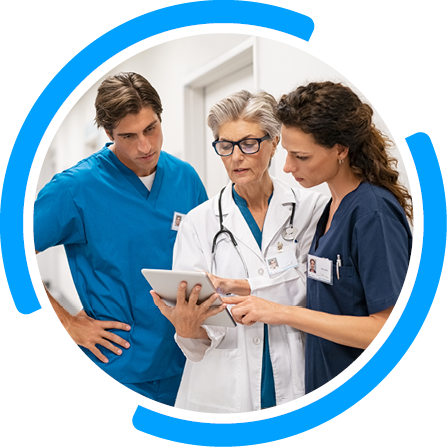

Serial biopsies to track tumor evolution and response to therapy can be helpful in informing treatment decisions, but can carry challenges, including complications from invasive diagnostic procedures2
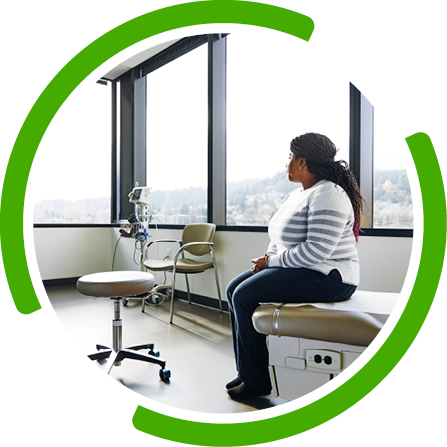

Testing for a broad array of DNA, RNA, and protein biomarkers is important for informing disease management, but tissue insufficiency can be a challenge2

NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer.
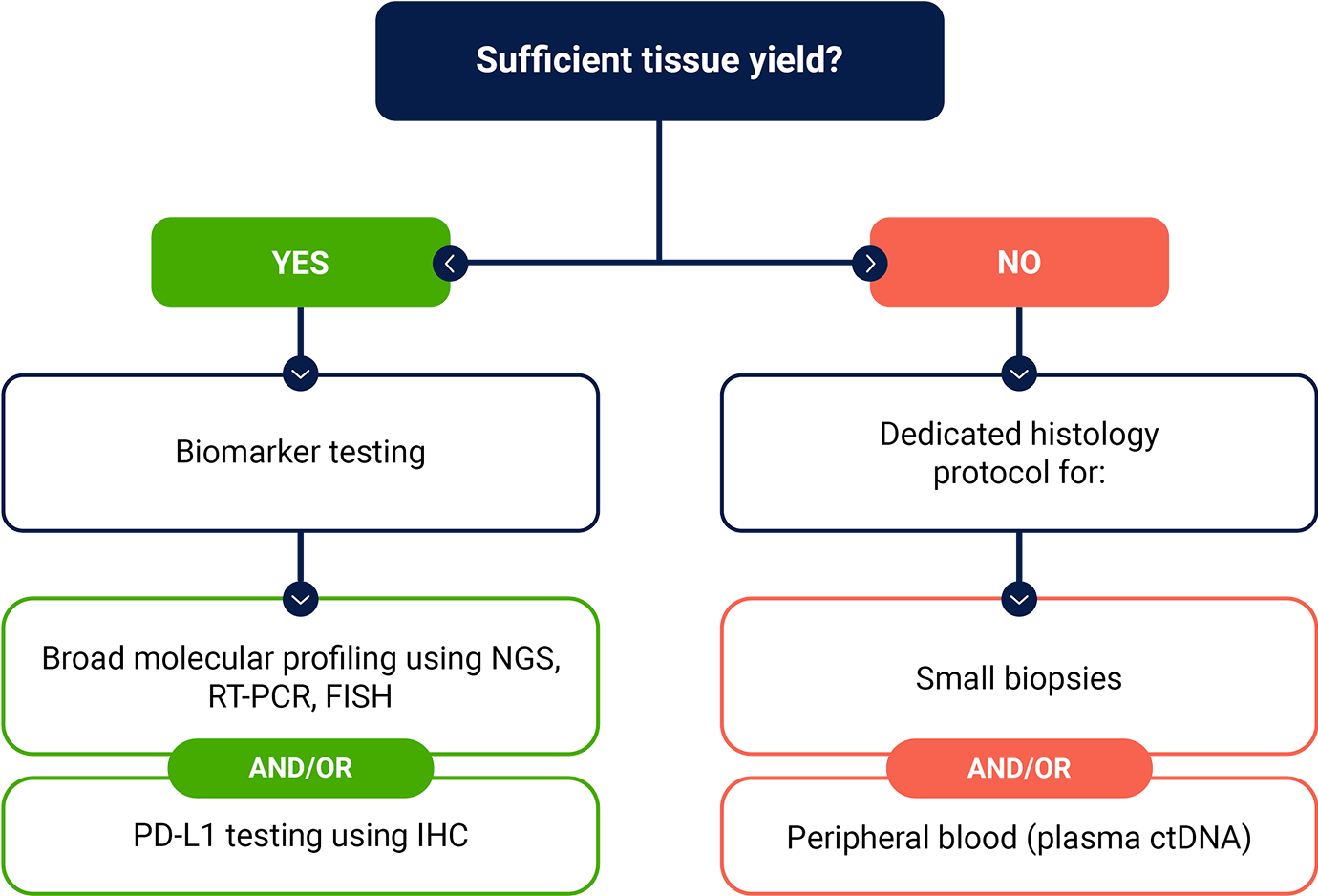
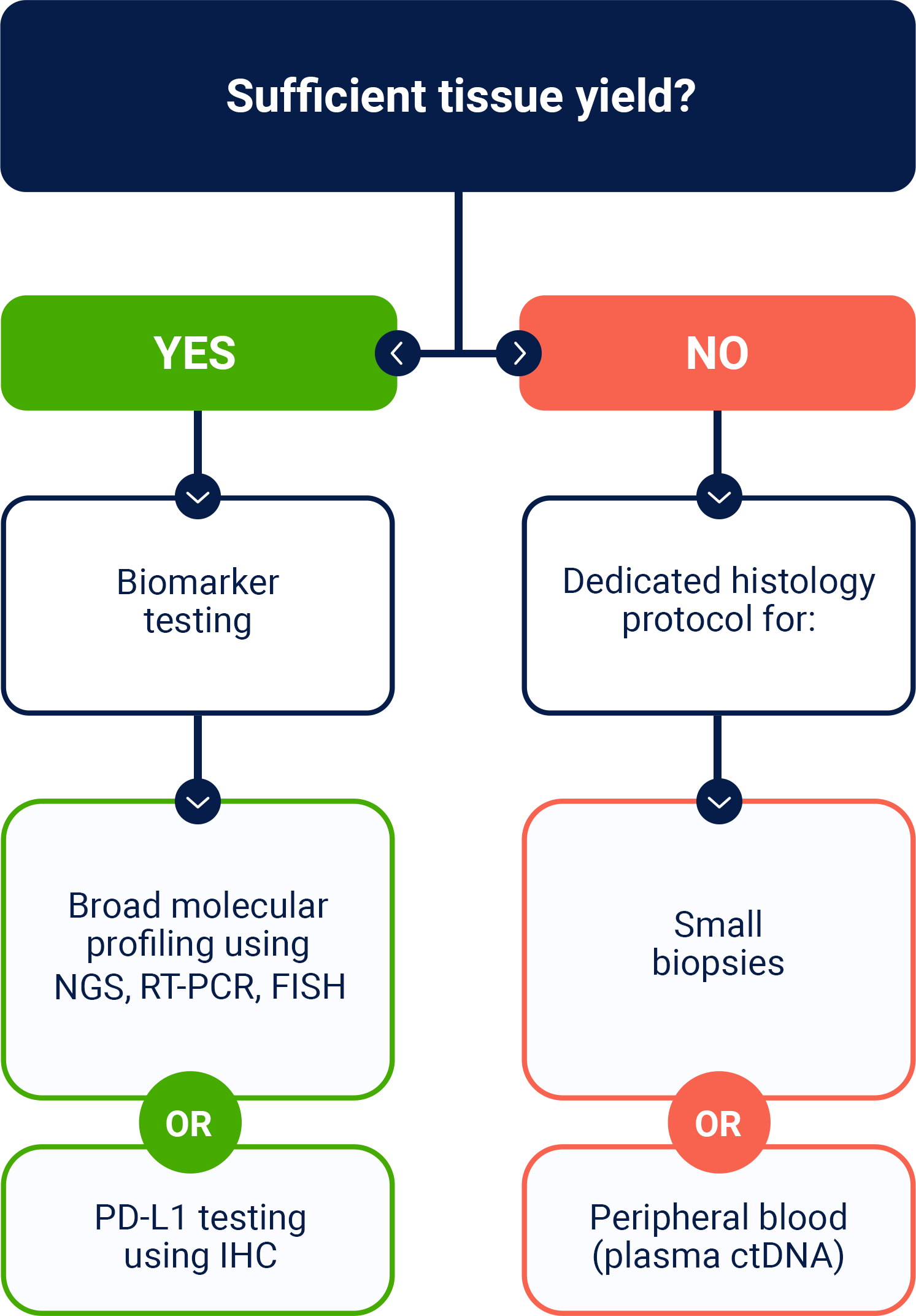
*Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V.3.2025. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2025. All rights reserved. Accessed March 31, 2025. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
ctDNA=circulating tumor DNA; FISH=fluorescence in situ hybridization; HCP=healthcare provider; IHC=immunohistochemistry; NGS=next-generation sequencing; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; PD-L1=programmed death-ligand 1; RT-PCR=reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.