Uses antibodies against tumor antigens to measure levels of protein
Utilizes fluorescent probes that bind to specific DNA sequences to identify chromosomal abnormalities
High-throughput method used to determine the nucleotide sequence of entire genomes or a broad panel of target genes
Used to amplify specific targets and detect alternative variants that lead to exon skipping
Determines the nucleotide sequence of DNA and is used when analyzing small regions of the DNA on a limited number of samples or genomic targets
ex14=exon 14; FISH=fluorescence in situ hybridization; IHC=immunohistochemistry; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition; NGS=next-generation sequencing; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; RT-PCR=reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
FFPE=formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded; H&E=hematoxylin and eosin; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition.
Stain images are provided by Roche Diagnostics.
IHC=immunohistochemistry; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition.
CEP7=centromere 7; FFPE=formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded; FISH=fluorescence in situ hybridization; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition.

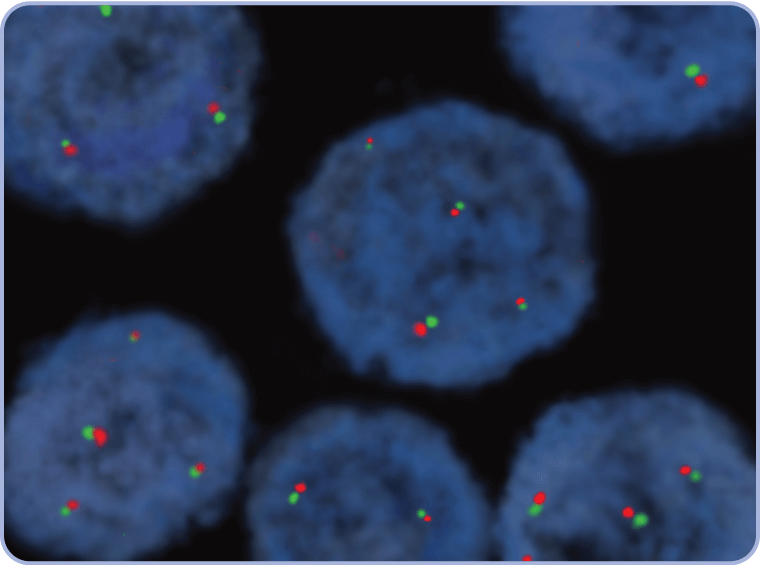

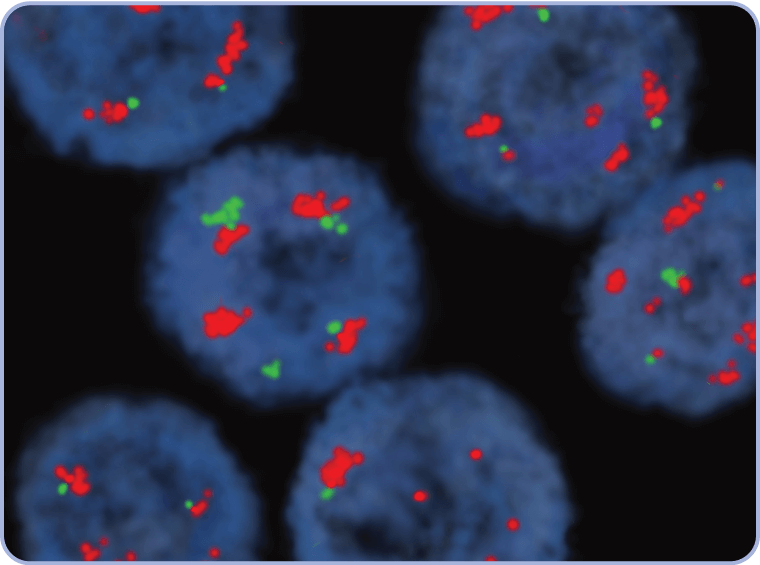

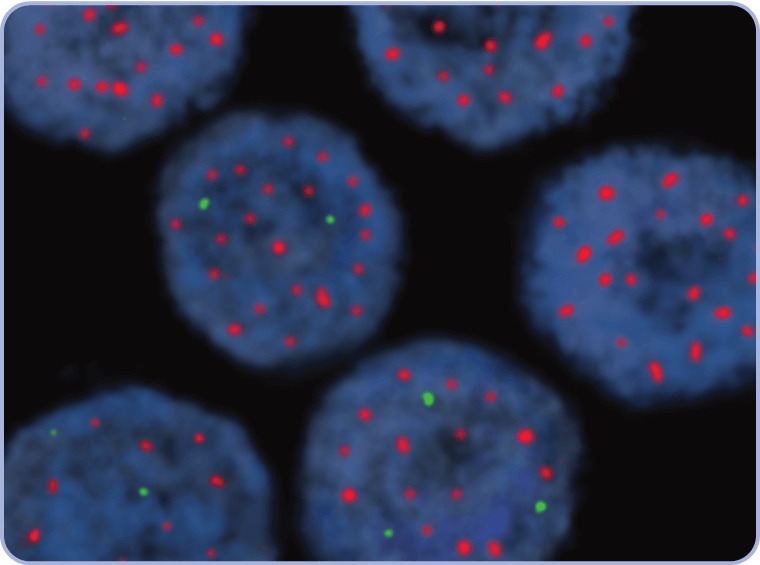

CEP7=centromere 7; FISH=fluorescence in situ hybridization; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition; WT=wild type.
ex14=exon 14; FFPE=formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition; NGS=next-generation sequencing.
ex14=exon 14; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition; NGS=next-generation sequencing; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer.
FFPE=formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition; NGS=next-generation sequencing.
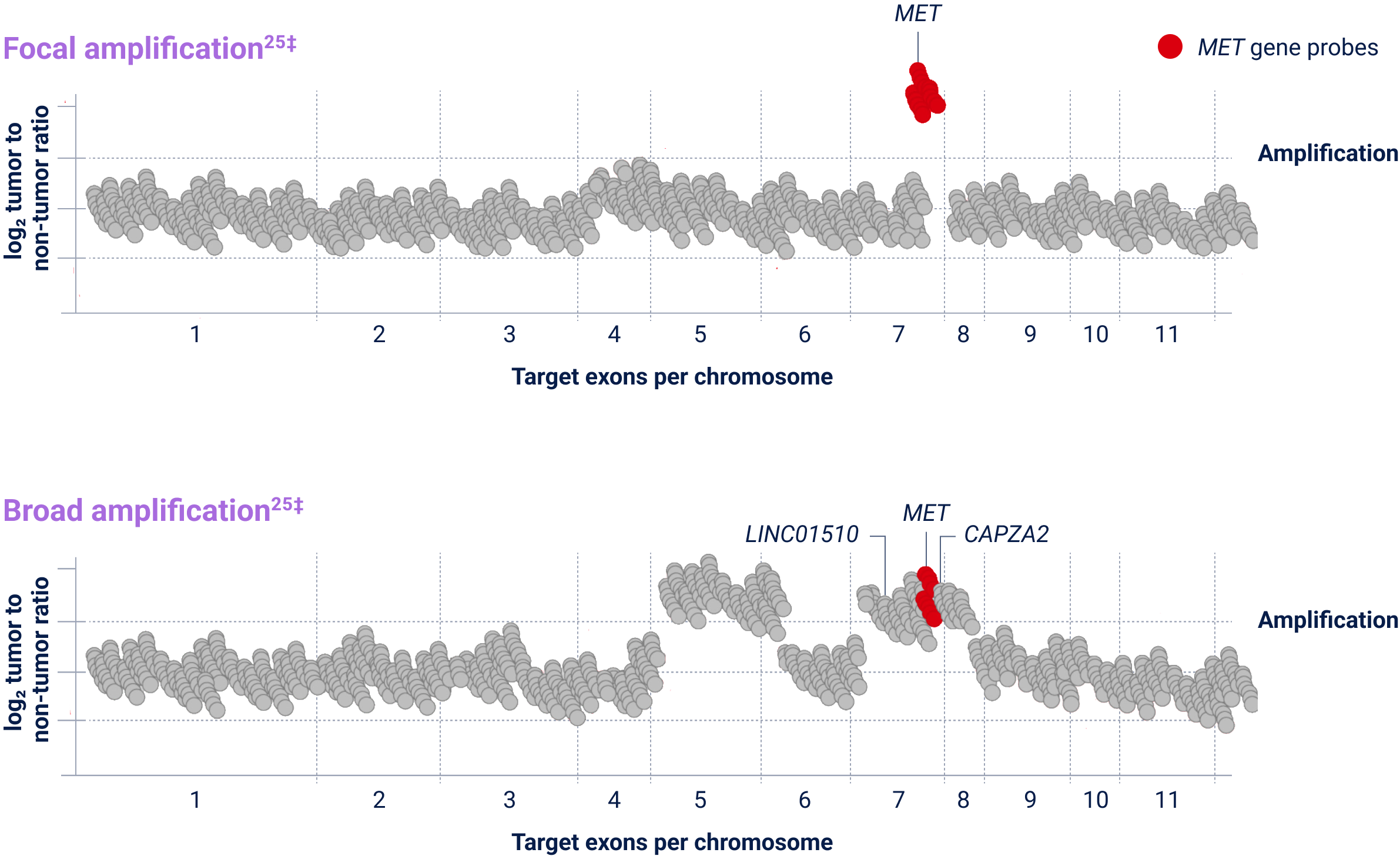
†The definition of high-level MET amplification is evolving and may differ according to the assay used for testing. Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V.3.2025. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2025. All rights reserved. Accessed March 31, 2025. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
CAPZA2=capping actin protein of muscle z-line subunit alpha 2; Chr=chromosome; LINC01510=long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1510; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition; NGS=next-generation sequencing.
MET amplification is an emerging biomarker and in clinical research as a potential therapeutic target. Some patients may have more than one MET aberration and may have overlap with other NSCLC biomarkers.