≥1% TPS
≥50% TC IHC3+
HER2 IHC3+
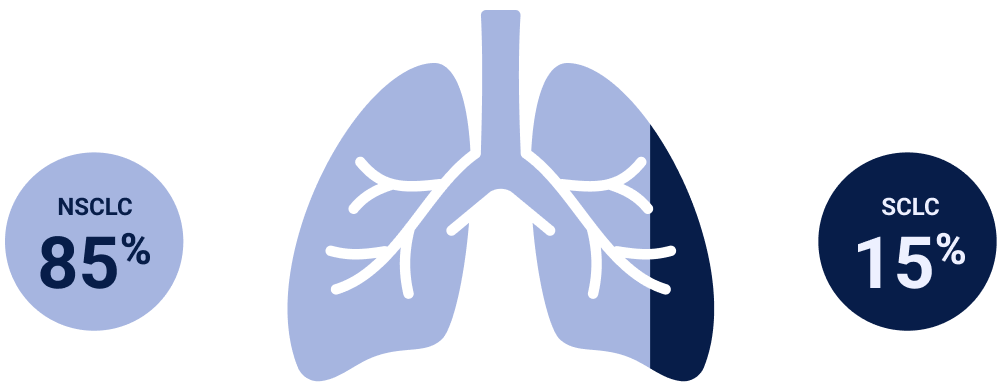
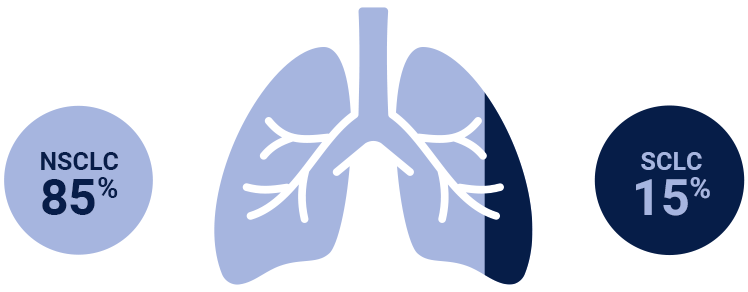
NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; SCLC=small-cell lung cancer.
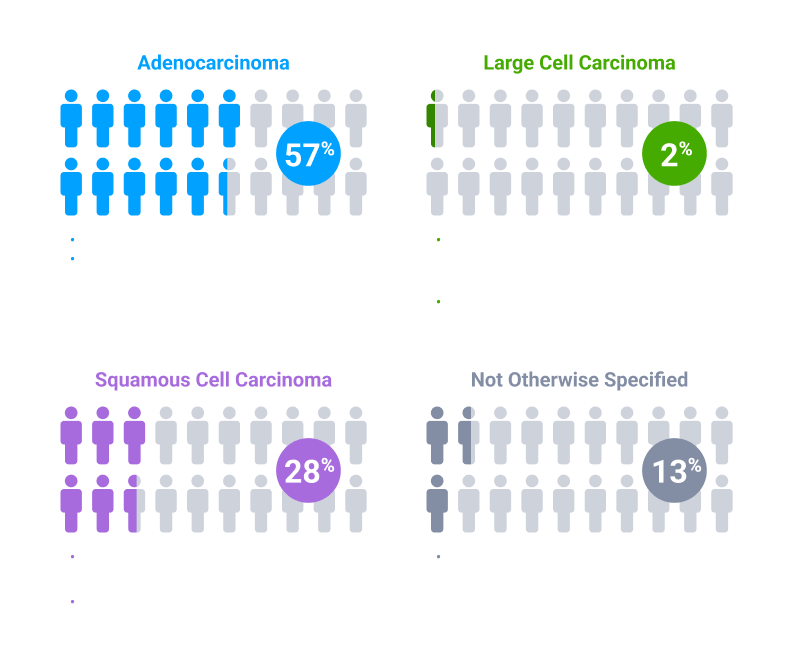
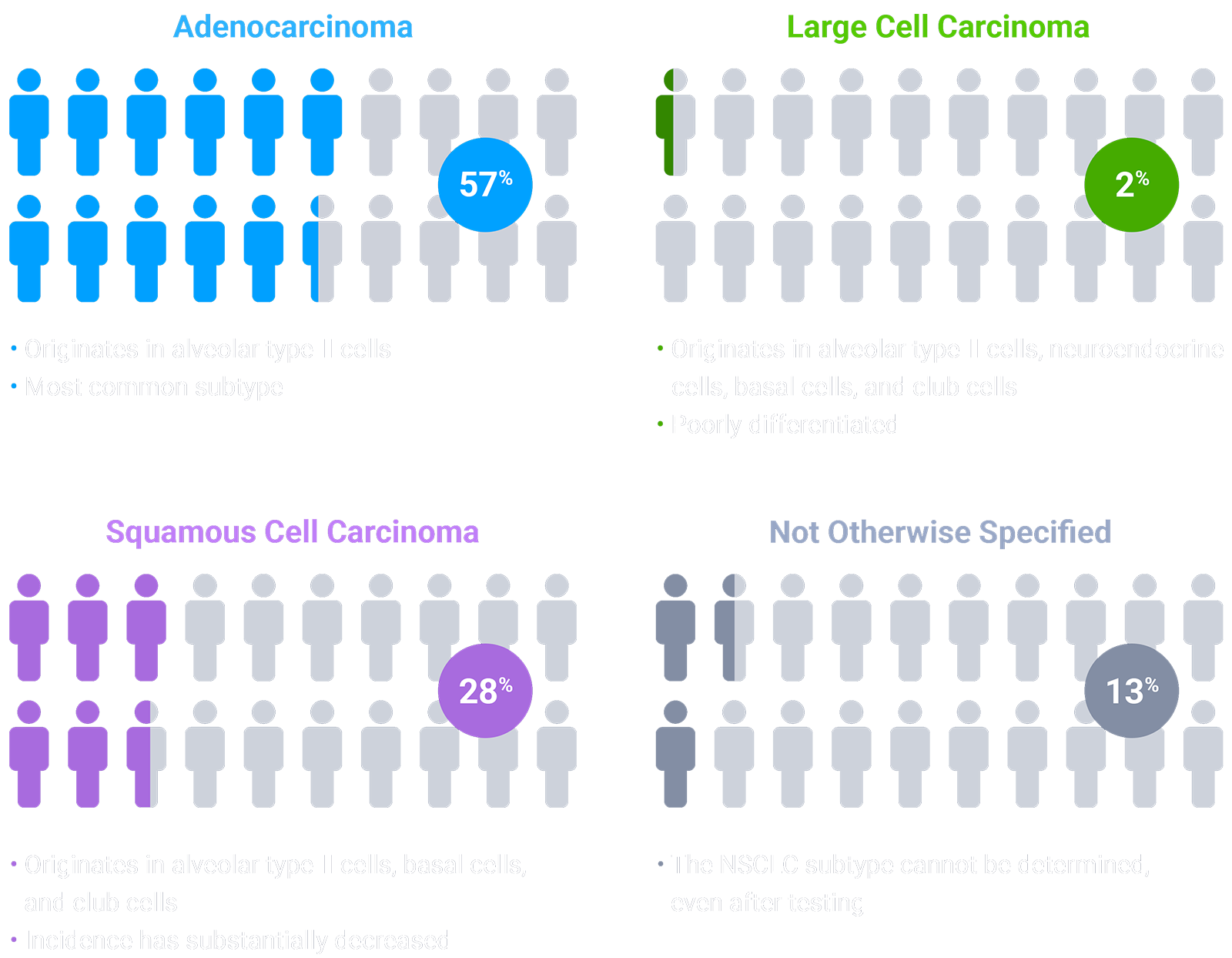
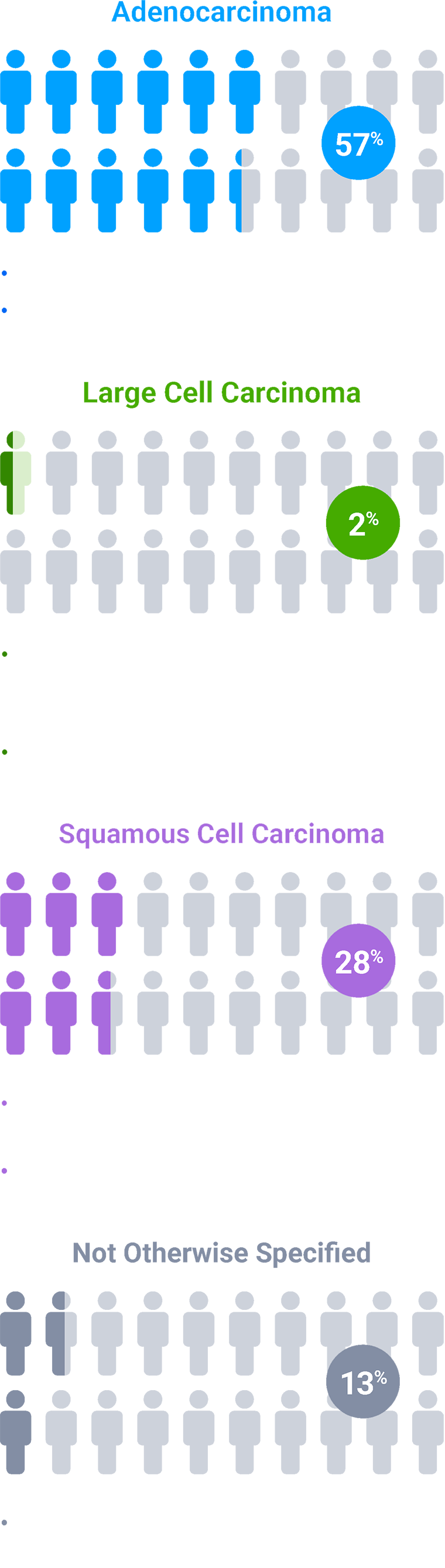
Colors indicate the estimated prevalence of NSCLC subtypes and are for illustrative purposes only. The model does not represent individual patients.
NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; SCLC=small cell lung cancer.
Currently, several testing options, such as NGS panels, are able to detect genetic alterations implicated in NSCLC. IHC testing represents a distinct methodology that captures changes in protein expression3
≥1% TPS
≥50% TC IHC3+
HER2 IHC3+
≥1% TPS
≥50% TC IHC3+
HER2 IHC3+
*Threshold for c-Met protein overexpression is ≥50% tumor cells with strong (3+) staining intensity. †EGFR-WT NSQ NSCLC.
EGFR=epidermal growth factor receptor; HER2=human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IHC=immunohistochemistry; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition; NGS=next-generation sequencing; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; NSQ=non-squamous; PD-L1=programmed death-ligand 1; TC=tumor cell; TPS=tumor proportion score; WT=wild type.
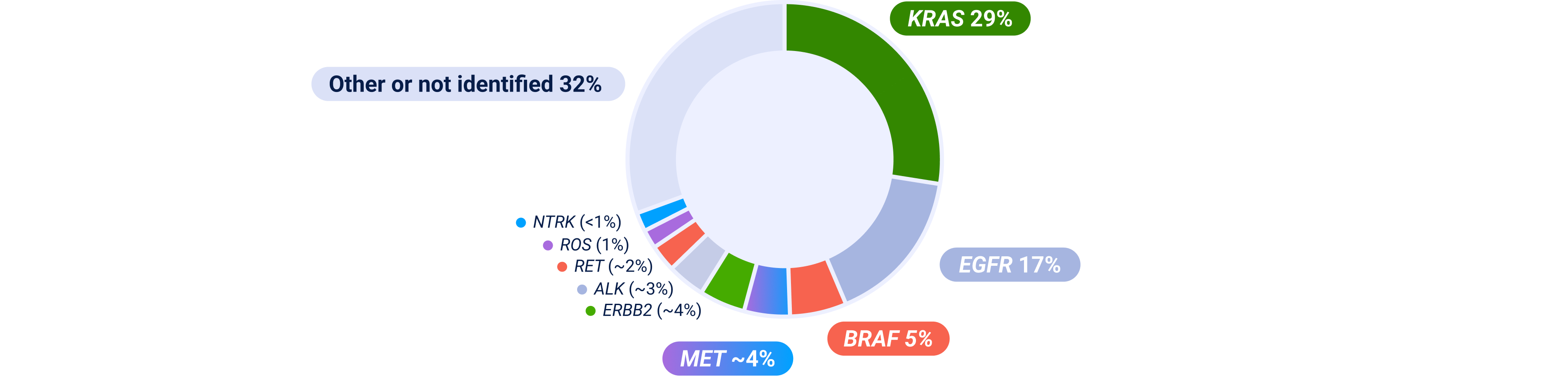
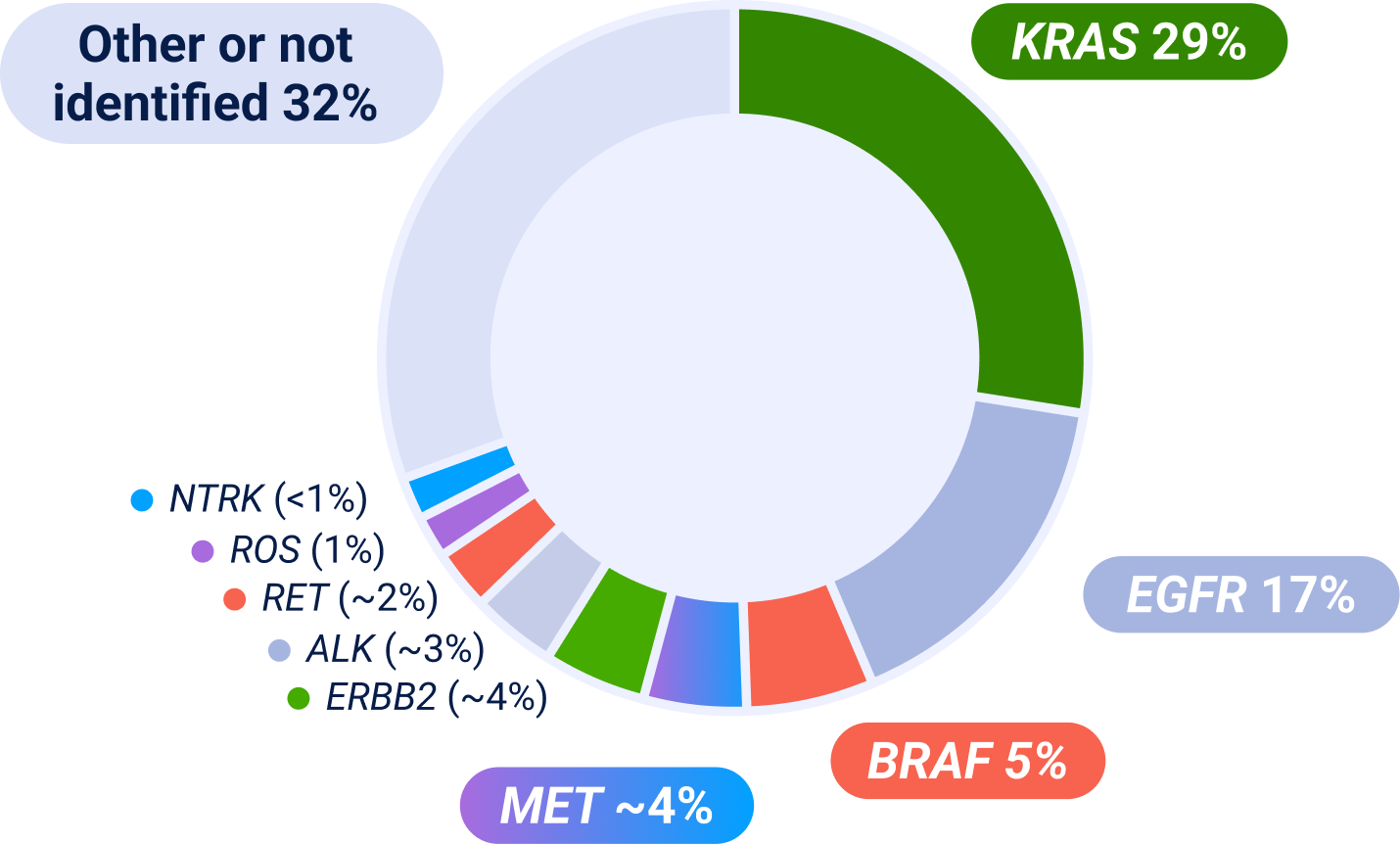
ALK=anaplastic lymphoma kinase; BRAF=B-Raf; EGFR=epidermal growth factor receptor; ERBB2=erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; IHC=immunohistochemistry; KRAS=kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; MET=mesenchymal-epithelial transition; NGS=next-generation sequencing; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; NTRK=neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase; RET=rearranged during transfection; ROS=ROS proto-oncogene.
Prevalence estimates are based on multiple sources; survival and prevalence data can vary among studies and datasets because of detection methodology used, patient sample sizes and/or demographics/characteristics. Some patients may have more than one MET aberration and may have overlap with other NSCLC biomarkers.